Many SaaS companies struggle to grow even after they invest in advertising, content, and multiple channels. Traffic comes in, demos are booked, but conversions remain low. In some cases, churn outweighs new signups. This usually happens when marketing efforts are conducted without a clear SaaS marketing strategy.
SaaS buyers take their time to decide. Before making a choice, they compare tools, read reviews, test products, and discuss with multiple stakeholders. Generic campaigns do not address these steps. Even strong products lose attention in crowded SaaS categories due to a lack of clear positioning and messaging.
This is where a structured SaaS marketing strategy can help. It integrates acquisition, activation, and retention into a single system. Many teams already use performance marketing software to track results. Strategy ensures that this data results in better decisions, not just reports. When marketing efforts match product value and buyer intent, SaaS growth becomes easier to predict and sustainable.
What Is a SaaS Marketing Strategy?
A SaaS marketing strategy is an in-depth plan that outlines how a software will be positioned, promoted, and developed during the product lifecycle. It is about attracting the right users, helping them to see value quickly, and keeping them engaged over time. Unlike short-term campaigns, this strategy focuses on long-term revenue and retention.
For SaaS businesses, marketing does not end with lead generation. It enables product adoption, trial conversions, renewals, and expansions. Every touchpoint is important, from the initial website visit to ongoing product usage. This is especially true for B2B SaaS, where purchasing decisions require research, comparisons, and internal approval.
A well-defined SaaS marketing strategy connects customer intent and business goals. It aligns channels, messaging, and content with how buyers evaluate software. It helps teams in setting priorities, cutting down on wasteful spending, and creating steady demand instead of depending on spikes from isolated campaigns.
How SaaS Marketing Differs From Traditional B2B Marketing
SaaS marketing uses a recurring revenue model. Unlike traditional B2B products, which rely on one-time transactions, SaaS growth is based on ongoing usage and renewals. Winning a customer is just the first step. Long-term value comes from retention and expansion.
Another major difference is in the buying process. SaaS buyers do extensive research before making a decision. They read comparison pages, review websites, and frequently test products via free trials or demos. Marketing must support this research phase with clear messaging and easily accessible content.
SaaS products are also frequently updated. Features evolve, pricing changes, and integrations expand. Marketing must stay on track with the product plan and communicate value consistently. This requires collaboration among product, sales, and marketing teams. Without this alignment, messaging becomes out of date, lowering user expectations.
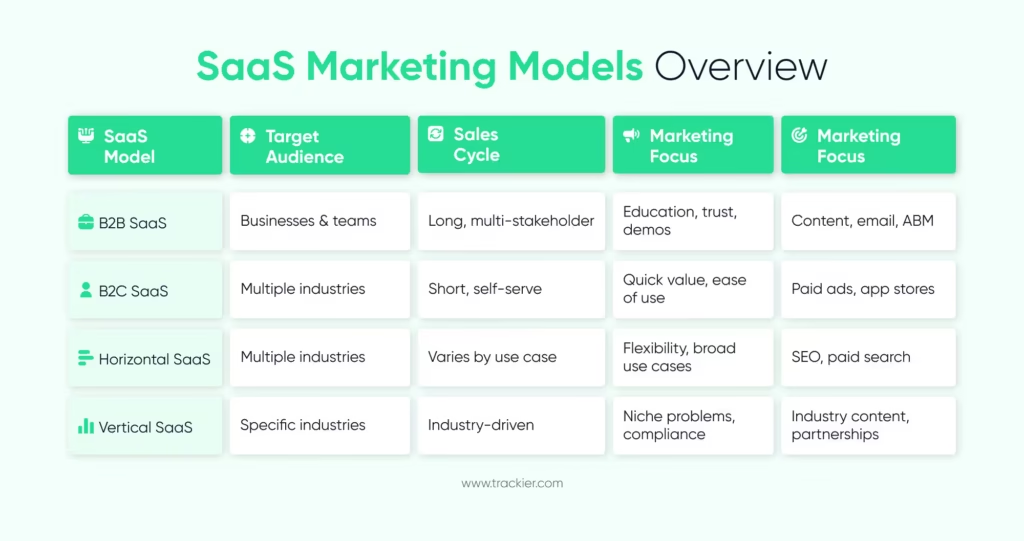
Types of SaaS Marketing Models
SaaS companies use different marketing models depending on their product, audience, and growth strategies. Choosing the right model supports teams to focus on channels and messaging that correspond to buyer behaviour.
B2B SaaS Marketing Strategy
A B2B SaaS marketing strategy focuses on businesses rather than individual users. The buying cycle is longer and involves a number of stakeholders, including decision-makers, end users, and finance departments. Rather than quick conversions, marketing prioritizes education, trust, and long-term value.
Case studies, product comparisons, and use-case pages are all important content in this context. According to Gartner, B2B buyers spend only 17% of their time meeting with suppliers during the purchasing process, relying heavily on self-guided research.
B2C SaaS Marketing Strategy
B2C SaaS marketing is focused on individual users and prioritizes volume. The decision-making process is faster, and the prices are usually lower. Marketing efforts prioritize ease of use, quick value, and emotional triggers.
Free trials, freemium designs, and app store visibility are more important in this approach. Retention remains critical, as users can easily switch tools if the value is unclear.
Horizontal vs Vertical SaaS Marketing
Horizontal SaaS products serve multiple industries. Marketing points out adaptability and broad use cases. Vertical SaaS products target a specific industry, like healthcare or fintech. Here, marketing focuses on industry-specific issues and regulatory requirements.
Vertical SaaS brands often notice higher conversion rates due to their prominent relevance. According to an OpenView study, vertical SaaS brands generate more revenue when their messaging focuses on specific pain points.
Understanding the SaaS Customer Journey
The SaaS customer journey describes how users go from discovering a product to becoming loyal customers. Treating all users the same frequently results in drop-offs, low conversions, and poor retention.
Awareness Stage
At this point, users are aware of the problem but may be unsure of the best solution. They search the internet, read blogs, and look for clear explanations. SaaS brands that show up early with useful content earn trust before competitors enter the picture.
Problem-solving blogs, guides, and educational pages do well here. The goal is to help users understand their problem, not to push a product too soon.
Consideration Stage
Users start comparing tools at this stage. They evaluate features, pricing, use cases, and reviews. They look for clarification and proof. Users are likely to ignore any content that appears vague or overly sales-driven.
Comparison pages, case studies, demos, and product walkthroughs are all useful in this context. Clear positioning helps users understand where the product fits and why it is appropriate for their needs.
Conversion Stage
During the conversion stage, users determine whether the product is worth paying for. Free trials, demos, and onboarding experiences all play an important role here. Users want to see the value right away without any inconvenience.
Simple onboarding flows, guided setups, and clear next steps increase the chance of conversion.
Retention and Expansion
SaaS growth depends on maintaining user engagement after they convert. When users continue to see value, they are more likely to renew, upgrade, or increase their usage.
Lifecycle emails, in-app training, and regular product updates keep customers engaged. Retention-focused marketing is more effective for long-term growth than constant new acquisition.
Crafting a Strong SaaS Go-To-Market Strategy
A SaaS go-to-market strategy describes how a product reaches the right customers and turns demand into revenue. Without a clear strategy, teams rely on disconnected campaigns and short-term successes. A structured approach helps marketing, sales, and product teams all work in the same direction.
What Is a SaaS Go-To-Market Strategy?
A SaaS go-to-market strategy describes how a product can be launched, positioned, and sold. The strategy focuses on who the product is intended for, how it addresses their problem, and which channels drive sales. This strategy becomes increasingly important as SaaS products grow and enter competitive markets.
A go-to-market strategy for B2B SaaS companies also specifies how marketing works with sales teams and how leads move through the funnel.
Core Elements of a SaaS Go-To-Market Strategy
Target market and ICP
Your ideal customer should be defined based on industry, company size, budget, and use case. A clear ICP helps teams to focus on high-intent buyers while avoiding wasted acquisition spend.
Buyer personas
Identify everyone involved in the purchasing decision, including end users, decision makers, and influencers. At each stage, messaging should be tailored to their specific goals and concerns.
Pricing and packaging
Pricing should be simple and transparent. Flexible plans reduce friction and help buyers move forward without lengthy negotiations.
Distribution channels
Select channels based on product complexity and duration of the sales cycle. This could include organic content, paid campaigns, partnerships, marketplaces, or direct sales outreach.
Product-Led, Sales-Led, and Hybrid GTM Models
Product-led go-to-market strategies are based on free trials or freemium models. Customers get to try the product before speaking with the sales team. This is ideal for simple products with quick onboarding.
Sales-led strategies revolve around demos and direct outreach. These are best suitable for complex SaaS products with higher price points and longer decision-making cycles.
Hybrid models combine the two approaches. Marketing generates demand, the product facilitates activation, and sales respond when users demonstrate strong intent. Many B2B SaaS companies use this model as they grow.
Core Pillars of an Effective SaaS Marketing Strategy
A SaaS marketing strategy works best when based on clear internal systems. These pillars focus on how teams plan, execute, and grow marketing efforts rather than buyer stages. Every pillar supports consistency, accountability, and measurable growth.
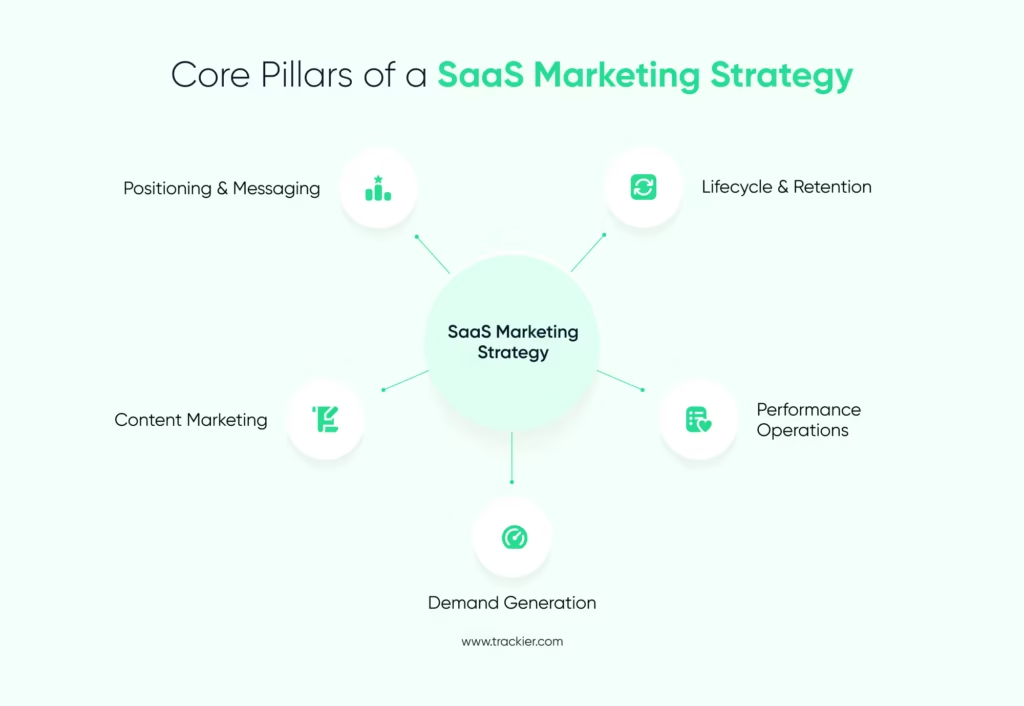
1. Positioning and Messaging
Positioning defines the product’s existence in the market and why it exists. It clarifies who the product is intended for and what problem it addresses. Without strong positioning, campaigns can draw the wrong audience or fail to convert.
Messaging converts positioning into actionable words. It influences website copy, advertisements, sales decks, and product pages. Clear messaging helps teams to communicate value without overexplaining or confusing buyers.
2. SaaS Content Marketing Strategy
Content serves as a long-term growth driver for SaaS businesses. A structured content marketing strategy ensures that blogs, landing pages, and resources serve specific business objectives.
This pillar focuses on:
- Topic selection is based on search intent and buyer questions
- Content formats are aligned with product complexity
- Consistent publication and optimisation
Strong SaaS content promotes brand awareness, trust, and inbound demand without relying solely on paid channels.
3. Demand Generation Systems
Demand generation is about creating repeatable systems, not one-time campaigns. This pillar outlines how demand is created, captured, and qualified.
This includes:
- Inbound lead capture through content and SEO
- Outbound efforts include targeted emails and partnerships
- Lead scoring and handoff procedures with sales
Clear demand generation processes remove team friction and gradually improve lead quality.
4. Performance and Growth Operations
Data, testing, and optimisation are important parts of performance marketing. This pillar focuses on how teams track and improve results across multiple channels.
It covers:
- Channel testing and budget allocation
- Conversion rate optimization
- Attribution and reporting frameworks
Growth operations ensure that decisions are made based on performance data rather than assumptions.
5. Lifecycle and Retention Operations
Retention marketing needs long-term processes rather than reactive campaigns. This pillar focuses on how SaaS teams retain user engagement after conversion.
It includes:
- Onboarding communication
- Product education workflows
- Engagement and constant support
Strong lifecycle operations improve product adoption and long-term revenue without increasing acquisition costs. A PLM platform makes this possible by connecting product development cycles directly to customer retention workflows.
SaaS Content Marketing Strategy
A strong SaaS content marketing strategy promotes long-term growth. It helps SaaS brands to stay visible, address buyer questions, and establish trust before a sales conversation begins.
Why Content Matters for SaaS Companies
Buyers of SaaS conduct research before committing. They want clarity, proof, and practical insights. Content can help meet these expectations without requiring direct sales involvement.
For SaaS teams, content helps:
- Organic discovery through search
- Education about complex products
- Clear differentiation in crowded markets
Well-written content also relieves pressure on sales teams by addressing common questions up front.
Content Types That Work Well with SaaS
Different content formats have different purposes. A balanced SaaS content marketing strategy uses a variety of formats based on intent.
- Blogs and SEO content: These appeal to users looking for solutions and comparisons. Consistent optimisation increases long-term visibility.
- Case studies and customer stories: These increase credibility and demonstrate how the product works in practical situations.
- Guides and resources: In-depth content helps users to better understand problems and solutions.
- Product content: Feature pages, walkthroughs, and documentation for easier evaluation and adoption.
Content Distribution Channels
Creating content is only part of the strategy. Distribution determines both reach and impact.
- Organic search continues to be an important channel for SaaS content.
- Email marketing helps to nurture leads and re-engage users.
- Social media platforms and communities promote awareness and conversation.
A clear distribution plan ensures that content reaches the intended audience without relying on guesswork.
B2B SaaS Marketing Strategies That Drive Revenue
B2B SaaS marketing values quality over quantity. The goal is to attract leads and generate demand that converts to revenue. Strong strategies align marketing efforts to sales results and long-term customer value.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
Account-based marketing can work for SaaS companies that target midmarket and enterprise customers. Rather than broad campaigns, ABM targets a specific set of high-value accounts.
The marketing and sales teams collaborate to:
- Personalize the messaging for each account
- Conduct targeted outreach across channels
- Track engagement at the account level
When used regularly, ABM improves conversion quality and shortens sales cycles.
Product Marketing and Sales Enablement
B2B SaaS growth depends mainly on product marketing. It ensures that features are clearly positioned and linked to actual use cases.
This includes:
- Launch messages and announcements
- Competitive positioning
- Sales enablement content, such as decks and one-pagers
When sales teams have the appropriate materials, conversations become focused and fruitful.
Partnerships and Integrations
Partnerships help SaaS companies reach new audiences. Integrations with complementary tools improve product value and visibility.
Co-marketing activities such as webinars, collaborative content, and marketplace listings support mutual growth. Strong partnerships boost credibility, particularly for newer SaaS brands.
SaaS Marketing Channels to Focus On
Choosing the right channels helps SaaS teams make better use of their available resources. The best SaaS marketing strategy ranks channels according to intent, cost, and scalability.
SEO and Organic Growth
SEO is still a reliable channel for SaaS growth. Buyers are actively looking for solutions, comparisons, and alternatives. Ranking for high-intent keywords leads to consistent traffic over time.
Well-structured blogs, product pages, and comparison content help with organic discovery. Regular updates help to keep visibility as search behaviour changes.
Paid Search and Paid Social
Paid channels help SaaS teams to generate demand quickly. Search ads attract high-intent users, whereas social ads promote awareness and retargeting.
Success here depends on:
- Clear landing pages
- Strong messaging
- Continuous testing
Paid channels perform best when they are well-positioned and have relevant content.
Email Marketing and Automation
Email is a useful channel for SaaS communication. It supports lead nurturing, onboarding, and ongoing engagement.
Automated workflows enable the delivery of timely messages with minimal manual effort. Segmentation increases the relevance and response rates.
Influencer, Community, and Review Platforms
Communities and review sites influence SaaS purchasing decisions. Buyers value peer feedback more than brand messaging.
Participating in relevant communities, collaborating with industry creators, and maintaining active review profiles all increase visibility and credibility.
Measuring SaaS Marketing Success
Measuring results enables SaaS teams to identify what is working and what needs to be improved. Without clear measurement, marketing decisions are based on assumptions. A structured SaaS marketing strategy uses predefined metrics to measure impact across enrollment, activation, and retention.
Key SaaS Marketing Metrics
SaaS marketing performance should be measured using metrics that link marketing activity to revenue.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Tracks the cost of acquiring a new customer. High CAC often indicates inefficient channels or poor targeting.
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): Refers to the total revenue a customer generates over time. Strong retention boosts LTV without increasing spend.
- The LTV to CAC ratio: Indicates whether acquisition efforts are sustainable. A healthy ratio indicates effective growth.
- Conversion Rates: This includes trial-to-paid, demo-to-close, and landing page conversions. These metrics identify friction points in the funnel.
Attribution and Funnel Visibility
Before converting, SaaS buyers go through a number of interactions. Attribution enables teams to understand which channels influence decisions.
Single-touch models simplify the journey. Multi-touch attribution provides greater insight into how content, paid campaigns, and outbound efforts interact. Clear attribution enhances budget allocation and channel optimisation.
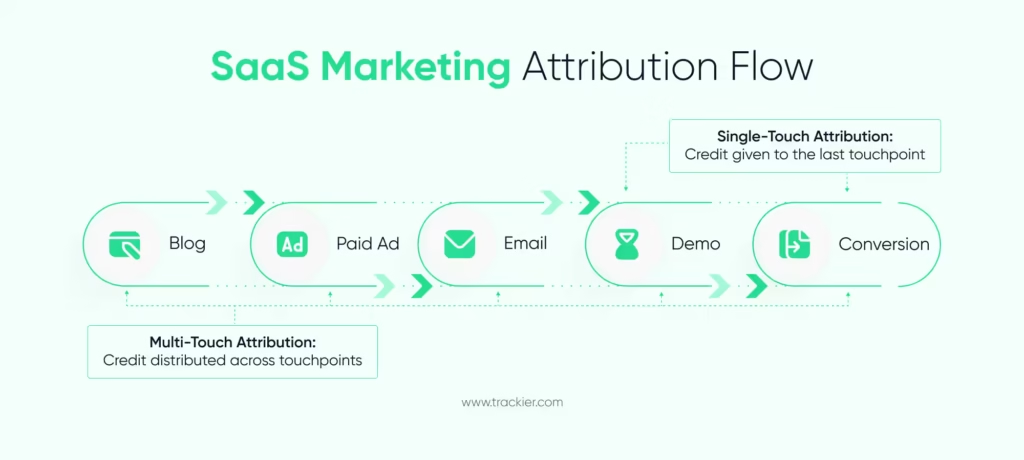
Using Data to Optimise SaaS Marketing Strategies
Data should drive action, not just reporting. SaaS teams must conduct regular reviews to identify patterns and gaps.
This includes:
- Growing channels to achieve consistent results
- Improve pages or campaigns with high drop-offs
- Aligning insights among marketing, sales, and product teams
Consistent measurement makes SaaS marketing strategies easier to refine and scale.
Common SaaS Marketing Mistakes to Avoid
Even well-funded SaaS teams struggle when basic errors are overlooked. These issues slow down growth, raise costs, and cause misalignment among teams.
Focusing on Vanity Metrics
High traffic or impressions can seem impressive, but they do not always indicate impact. Metrics that do not relate to conversions or revenue provide very little insight. SaaS marketing strategies are better when success is measured by qualified leads, activation, and retention.
Poor ICP Definition
Targeting a large audience weakens messaging and raises acquisition costs. Without a specific ideal customer profile, marketing attracts users who are unlikely to convert or stay. Defining ICP early improves lead quality and campaign efficiency.
Overinvesting in Acquisition and Ignoring Retention
Many SaaS companies choose new user acquisition over existing customer retention. Churn reverses acquisition, making growth unstable. Retention-focused efforts boost long-term revenue without increasing spending.
Inconsistency in Sales, Marketing, and Product
When teams work in isolation, the messaging becomes inconsistent. Leads are misqualified, and users face gaps between expectations and product experience. Alignment across teams leads to smoother handoffs and clearer communication.
Relying on Short-Term Campaigns
One-time campaigns can end up in temporary increases, but they do not lead to long-term growth. A strong SaaS marketing strategy prioritises repeatable systems over one-time wins.
Future Trends in SaaS Marketing
SaaS marketing keeps changing as buyer behaviour, privacy norms, and technology change. Teams that adjust quickly have an advantage in crowded markets.
Increased Focus on Personalisation
Buyers expect relevant messaging tailored to their role, industry, and intent. Personalised content and campaigns boost engagement without increasing volume. SaaS teams are investing more in segmentation and behavior-based targeting.
Privacy-First Marketing Approaches
Data privacy regulations are changing the way SaaS marketers collect and use data. First-party data strategies are increasingly important. Consent-based tracking and transparent data usage help to maintain trust.
Revenue-Driven Marketing Teams
Marketing teams are increasingly being evaluated on revenue impact rather than lead volume. This shift requires teams to work closely with sales and prioritize pipeline contribution, activation, and retention.
Improved Product-Marketing Integration
Product insights now have a more direct impact on marketing decisions. Feature adoption, usage data, and feedback loops all help to refine messaging and prioritize campaigns.
Conclusion
A SaaS marketing strategy works when it is focused, structured, and aligned with actual business objectives. Growth becomes predictable when teams understand their market, communicate value clearly, and invest in long-term scalable systems.
Successful SaaS businesses rely on strong positioning, regular updates, and visible demand generation. They prioritise retention with acquisition and avoid chasing short-term gains. As markets become increasingly competitive, clarity and execution are more important than volume.
FAQs
What is the 3-3-2-2-2 rule of SaaS?
The 3-3-2-2-2 rule of SaaS describes how growth typically occurs. SaaS companies aim for 3x growth in early stages, followed by another 3x once the product stabilizes. Growth slows to 2x over the next three phases as markets mature, competition rises, and growth prioritizes efficiency, retention, and predictable revenue.
What is SaaS marketing?
SaaS marketing refers to the strategies and channels used to promote, sell, and maintain software available on a subscription basis. It focuses on recurring revenue, long purchase cycles, and ongoing engagement. SaaS marketing promotes discovery, product adoption, renewals, and growth by matching messaging, content, and channels to how users evaluate and use software.
What are the four marketing strategies?
The four most common marketing strategies are market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification. Market penetration focuses on increasing sales to existing markets. Product development introduces new features or products. Market development is meant to reach new audiences. Diversification involves bringing new products into new markets to reduce reliance on a single revenue source.
What is B2B SaaS marketing?
B2B SaaS marketing focuses on selling subscription-based software to businesses. It focuses on teams and decision-makers rather than individual users. The strategy is based on education, trust building, and clear use cases. Content, demos, account-based marketing, and sales alignment are critical in enabling longer sales cycles and higher-value contracts.



