User generated content marketing focuses on content created by individual users rather than brands. This includes reviews, social media posts, videos, photos, and feedback from customers about their experiences. For many brands, this type of content appears more natural to audiences and is easier to trust. People frequently consult other users before making a decision, particularly when comparing products or services.
User generated content marketing supports measurable results. When combined with tools such as performance marketing software, brands get an understanding of how user generated content influences clicks, conversions, and repeat actions. Instead of relying solely on polished brand creatives, businesses are now using customer feedback to increase visibility and growth. This approach is consistent with how people consume content on a daily basis and make purchasing decisions.
What Is User Generated Content Marketing?
User generated content marketing is the usage of content created by customers, users, or communities in a marketing campaign by a brand. The content is fully voluntary and based on actual experiences. Brands can collect, compile, and share this content across their channels with the proper permission.
Unlike brand-owned content, user generated content reflects personal perspectives and experiences. It is easier for other people to relate to. Around 79% of consumers say user generated content has a significant impact on their purchasing decisions, and 60% believe UGC is the most authentic form of marketing.
User generated content marketing goes beyond simply resharing posts. It involves deciding how customer content will fit into campaigns, product pages, advertisements, and communication channels. Brands promote users to share their experiences, and that content is utilized to increase engagement and conversion.
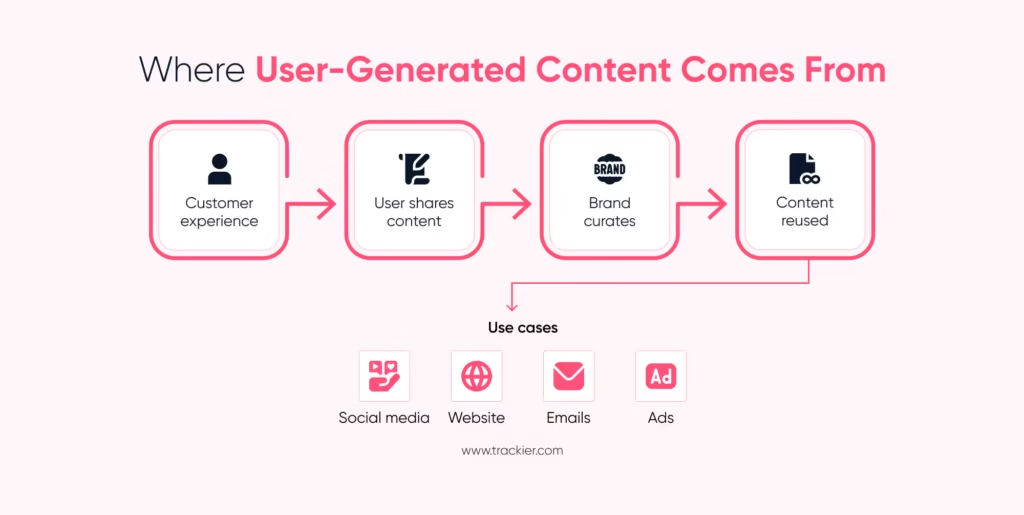
This type of marketing works well throughout the funnel. User generated content marketing is great for promoting awareness. It builds confidence while in consideration. Reviews and testimonials often influence final decisions. When used consistently, user generated content marketing transforms into a long-term asset rather than a one-time strategy.
Types of User Generated Content in Marketing
User generated content marketing works across formats because users share content in multiple formats. These formats are planned, while others develop naturally. For brands that understand and manage these formats, it becomes easy for them to reuse their content without asking for participation.
Social Media User Generated Content
Social media is the most preferred source of user generated content. This applies to posts, stories, reels, short videos, comments, and tagged mentions. Users often talk about their experiences without being asked, particularly after a positive interaction.
Branded hashtags make this content easier to find and reuse. When users tag a brand or use a campaign hashtag, it indicates their willingness and intent to participate. This format is effective for raising awareness and engagement because it appears native to the platform and blends easily into regular feeds.
Reviews & Ratings
Reviews are one of the most reliable forms of user generated content marketing. They are found on product pages, marketplaces, apps, and review sites. Many consumers use reviews as a quick checkpoint before moving forward.
Detail is what makes reviews so effective. Users frequently discuss what worked, what did not, and what they wish they had known sooner. This allows others to set realistic expectations and feel more confident in their decision. Reviews also address common concerns that brand descriptions usually miss, such as usability, delivery experience, and long-term value.
Visual and Video User Generated Content
User images and videos provide insight into the usage of the product after purchase. This includes unboxing videos, tutorials, before-and-after photos, and daily usage videos. Visual UGC helps to establish realistic expectations and builds credibility.
Short-form video platforms have increased the format’s value. Many brands now reuse customer videos in advertisements, websites, and social media because they are more relatable than studio-made visuals.
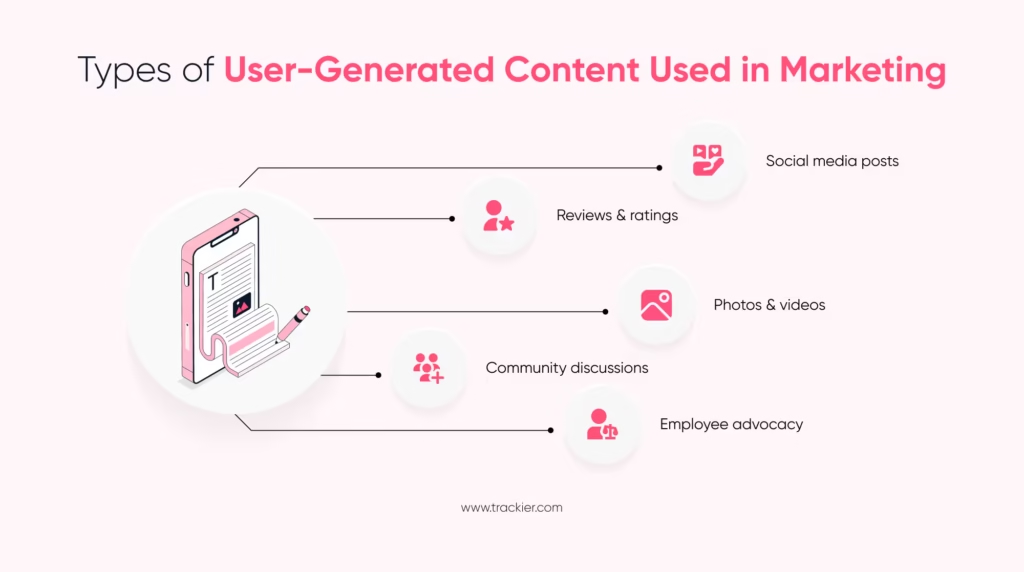
Community and Discussion-Based Content
Forums, comment sections, Q&A platforms, and brand-owned communities create community-generated content. Users share their thoughts, advice, and experiences voluntarily. This type of content fosters long-term trust and enables brands to better understand customer concerns.
Discussion-based user generated content marketing is especially beneficial for products or services that require explanation or comparison. It also encourages organic discovery via search and community platforms.
Employee and Internal Advocacy Content
Employee-generated content has a connection with user generated content, despite the fact that it originates within the organisation. Employees provide behind-the-scenes content, product usage, and office life. Though it is different from customer UGC, it does provide a human perspective. It works best when employees share freely, rather than through scripted posts.
Why User Generated Content Marketing Works
User generated content marketing is important as people look for opinions, experiences, and proof before trusting a brand. Content created by other users satisfies all these in a natural and non-compelling way.
Builds Trust Through Real Experiences
Trust is one of the primary reasons why user generated content marketing works so well. Customer-shared content reflects actual usage and honest opinions. It demonstrates how a product or service is used in everyday situations.
Unlike brand-created content, UGC does not appear scripted. Small details such as personal speaking style, natural visuals, and raw feedback increase credibility.
Encourages Higher Engagement
User generated content is often more engaging because it feels familiar. People tend to like, comment on, and share content created by people who share their interests. This type of interaction on social media platforms also helps in the organic promotion of content to larger audiences.
When users see their content featured by a brand, it leads to more users engaging with it. This creates a cycle in which more users contribute, increasing visibility and interaction without requiring additional effort from the brand.
Supports Better Decision-Making
During the consideration stage, User generated content marketing plays an important role. Reviews, photos, and videos provide practical answers that influence decisions. Users get a better understanding of quality, fit, usability, and results.
Seeing that multiple users have had similar experiences also reduces doubt. It reassures potential customers that their standards are reasonable and achievable.
Fits Naturally Across Marketing Channels
User generated content marketing is simple to adapt across channels. The same piece of content can be used across social media, websites, emails, and paid campaigns. Because it already feels natural, it does not disrupt the user experience.
This adaptability lets brands maintain consistency while also establishing their messaging in real user voices.
Benefits of User Generated Content Marketing
User generated content marketing gives practical benefits beyond visibility. When used consistently, it builds trust, engagement, and long-term brand growth without complicating the content process.
Improves Brand Credibility
One of the major advantages of user generated content marketing is credibility. User generated content seems honest because it reflects real-life experiences. When potential customers see others discussing a brand in their own words, it reduces hesitation and builds confidence.
User generated content marketing helps brands to appear more transparent. Displaying genuine feedback, images, and opinions makes the brand seem accessible and dependable.
Strengthens Customer Relationships
Sharing user content makes customers feel valued. It shows how the brand is paying attention to its users. This recognition promotes loyalty and repeat engagement.
Over time, this develops a sense of community. Customers are more likely to interact with a brand that actively interacts with them than with one that simply sends out messages.
Increases Engagement Across Platforms
User generated content gets more interaction because it is relatable. People are more likely to engage with content that they personally connect with. Users tend to comment, share, or save content created by people who are similar to them.
This engagement also promotes organic reach, particularly on social platforms where interaction signals are important.
Supports Conversion and Retention
UGC helps users in their decision-making process. Reviews, testimonials, and real-world scenarios answer questions that influence purchasing decisions. This minimizes hesitation in buying and increases conversion rates.
After purchase, continued exposure to user generated content marketing helps in retention. Seeing others share their positive experiences supports the customer’s decision.
Reduces Content Creation Pressure
User generated content marketing eliminates the need for ongoing in-house content creation. Companies can rely on their audience to share their experiences naturally.
This helps marketing teams to focus on selection, placement, and optimisation rather than creating everything from scratch.
User Generated Content Strategies That Work
When brands approach user generated content marketing as a deliberate effort rather than a passive outcome, it produces results. The right strategies help in the collection of better content, maintaining a level of quality, and the alignment of UGC with marketing objectives.
Create Clear Opportunities for Users to Share
Most users are willing to share content, but they require a clear reason and a simple method to do so. Simple prompts following a purchase, during onboarding, or after a service interaction are helpful. You reduce guesswork by asking users to submit images, comments, or brief videos.
It is important to provide clear instructions. When users understand where to post, what to tag, and how their content can be used, participation increases without difficulty.
Use Branded Hashtags and Campaign Prompts
Branded hashtags help in organizing user generated content and make it easier to locate it. They also provide a simple way for users to participate without requiring direct communication.
Campaign-based prompts are suitable for gathering large amounts of user generated content. They can be seasonal, product-focused, or experience-driven. Keeping the request simple improves both participation and content quality.
Encourage Without Over-Incentivising
Incentives can help to increase participation, particularly for new campaigns. High rewards, on the other hand, have an impact on authenticity. Small gestures like features, shoutouts, and early access are more effective than cash-based incentives.
The goal is to encourage genuine sharing over scripted responses. Content should reflect real-life experiences, even if it is not perfectly polished.

Curate and Moderate Thoughtfully
Not all user generated content should be used. Brands should select content that is consistent with their message and audience expectations. This includes evaluating the quality, relevance, and tone.
Moderation promotes consistency without sacrificing authenticity. Light editing for clarity is acceptable, but excessive editing can damage credibility.
Repurpose User Generated Content Across Channels
A single piece of user generated content can be reused across multiple channels. Social posts may appear on websites. Customer reviews can be added to product pages. Videos are great for advertisements or email campaigns.
Repurposing is time-efficient and ensures consistent messaging while remaining user-focused.
Acknowledge and Credit Contributors
Giving credit is an important part of user generated content marketing. Tagging or mentioning users promotes generosity and encourages others to participate.
Acknowledgement also increases trust between brands & users. It demonstrates that the brand respects ownership and appreciates the effort users put into creating content.
User Generated Content Marketing Across Channels
User generated content marketing works best when it is reused rather than posted once and forgotten. Brands don’t need a large budget or daily production to do this. All they need to share content where their target audience already spends time. Every channel serves a different purpose, and UGC helps each one in a unique way.
1. Social Media
User generated content and social media complement each other well because they both rely on interaction. A simple repost, duet, or hashtag campaign is a way to attract additional users to participate. Instead of polished brand posts, authentic customer content feels more familiar and trustworthy.
What works here: Reviews, product trials, unboxing videos, experience posts, hashtag entries, and comments.
How to use UGC on Social:
- Repost customer photos and videos with credit
- Share stories or reels with real experiences
- Highlight comments as posts to demonstrate authentic feedback
- Set up hashtag-driven UGC pools for discovery
2. Websites & Landing Pages
User generated content marketing on websites helps visitors make faster decisions because they can see proof from real users rather than branded claims. Even a single line of customer feedback can reduce hesitation.
Best formats: star reviews, photos, short quotes, embedded social posts, and short video clips.
Where to add UGC on websites:
- Homepage’s social proof strip
- Product/service pages as actual experience snapshots
- “Why Customers Choose Us” section, with quotes
- Case examples displayed next to CTAs for reassurance
3. Email Marketing
Email does not require lots of user generated content. Smaller pieces, such as a single sentence, screenshot, or visual, work best. It breaks up the monotony of brand-specific messaging and demonstrates that people actually use what is being promoted.
Where to plug UGC inside emails:
- Testimonial spot near a CTA
- Product launch emails to include social proof
- Cart recovery emails include a real user quote
- “Before you buy” educational email with UGC example
4. Ads and Paid Campaigns
Brands invest a lot of money in advertising. If the content looks too perfect, people will scroll. User generated content marketing makes ads feel more authentic and less sales-driven, which usually leads to increased attention and clicks. Even one short clip from a customer is enough to build curiosity.
How to repurpose UGC in ads:
- 5-10 second review clips as hooks
- Split-screen UGC along with product value point
- Ad copy that uses real user language rather than brand tone
- Screenshot of feedback for social proof
5. Community Spaces
User generated content marketing spreads faster in communities because people want to share something that helped them. These spaces serve as mini ecosystems where brand usage grows naturally. This is best suited for products or services that address ongoing issues.
Community-driven UGC examples:
- Tutorial posts explain how users solved issues
- Before/after experience stories
- Simple guides created by customers
- Peer recommendations within comment threads
6. Offline Channels
UGC isn’t is not exclusively online. A review can be printed on the packaging or a testimonial could appear in-store. A QR code can open a gallery of customer examples. If the content is good, there are no channel limitations.
Where offline UGC fits:
- On-box packaging reviews
- Event banners with customer quotes
- Checkout displays with QR to UGC gallery
- QR codes on receipts or pamphlets push customers to share content
User generated content marketing across channels does not require extensive production or complicated setup. It simply requires identifying where customers already speak, picking what sounds natural, and placing it where it reduces uncertainty.
For this reason, a lot of companies that use performance marketing software add user generated content into their funnels because proof at the appropriate time can influence conversions.
Consumer-Generated Content Marketing vs Influencer Marketing
User generated content marketing often gets compared to influencer content, but both serve different objectives within a marketing system. One is built on everyday users sharing their honest experiences, and the other is built on visibility through people with an audience. Both are useful, but the approach, cost, and outcome are not the same.
Consumer-Generated Content
Consumer-generated content is created by actual customers who don’t get paid for their efforts. It’s informal, unfiltered, and based on actual use. This is why it feels more relatable, and many brands receive positive feedback when they share it.
Examples:
- Customers post about their purchasing experience
- Short reviews or product trials
- Before/after results shared by users
- Social posts without brand involvement
- Screenshots for comments and feedback
Why do brands use it?
- Low or no cost to collect
- Easy to repurpose without much editing
- Works better for trust and validation
- Helps answer doubts before making a purchase
Influencer Content
Influencer content is made by creators who already have an audience. They either collaborate with brands or are paid to post. It helps businesses to reach new people faster, particularly when they need expansion or increased awareness.
Examples:
- Sponsored posts and videos
- Affiliate recommendations
- Niche creator tutorials or demos
- Story takeovers or collaborative brand campaigns
Why brands use it:
- Immediate access when entering a market
- Increased control over message and content quality
- Ideal for product education and launches
- Useful for channels with slow organic reach
Where Each Performs Best
| Goal | Consumer-Generated Content (UGC) | Influencer Content |
| Trust & Proof | Very Strong | Moderate |
| Lead Generation | Strong | Strong |
| Awareness Boost | Moderate | Very Strong |
| Conversion Support | Very Strong | Strong |
| Cost Efficiency | Very Strong | Moderate |
Consumer UGC typically works at the bottom of the funnel (decisions and conversions), whereas influencer content works at the top of the funnel (reach and discovery). When used together, they can close gaps in trust and awareness without relying solely on paid campaigns.
Which One Should a Brand Prioritise?
- If the goal is reach, collaborations help more.
- If the goal is trust, consumer UGC performs better.
- If the goal is conversion, combining both is the best option.
Many businesses are including consumer-generated content into paid campaigns because it appears natural and does not feel overly produced.
This is why performance marketing software is important. It can help in deciding which content influenced a result, rather than simply showing what received the most likes. It becomes easier to set up budgets based on outcomes rather than assumptions.
How to Collect User Generated Content
Collecting user generated content does not require much coordination or a dedicated team. Most of the time, customers are already sharing their experiences, but brands are missing out because they are not actively tracking them or providing users with a clear way to submit content. The most straightforward approach is to create simple entry points where content naturally flows in, and then curate from there.
1. Ask Directly and Make the Request Clear
People are more likely to share when the request is simple and specific. A simple instruction like “Share your experience using this hashtag” or “Tag us for a feature” is sufficient. Over-explaining usually prevents users from participating.
What works:
- One-line instructions for social media posts
- A callout on packaging or inserts
- A pinned comment requesting reviews or photos
- A highlight or story focused on customer features
2. Use Hashtags and Mentions to Centralise Content
Hashtags and mentions are the framework for organizing user generated content. They help brands in finding, collecting, and sorting content without having to search manually repeatedly.
Simple approaches:
- A branded hashtag for all submissions
- A unique campaign hashtag for each initiative
- Mentioning the brand to qualify for features
- Tracking mentions weekly to prevent missing posts
3. Create a Submission Point Users Can Reach Easily
Some users prefer to send content privately rather than publicly. Offering a simple route for this increases the amount of content a brand receives.
Submission options:
- Google Form or Typeform with 4–6 fields
- Email ID dedicated to customer stories
- In-app or website upload point
- Dropbox or WhatsApp for instant sharing
It should take less than one minute to submit. Participation decreases as the process becomes longer.
4. Build a Consistent Credit-and-Feature System
Users share regularly when they understand what happens after they submit. If the brand acknowledges and credits the original creator, it builds trust and encourages repeat participation without offering incentives.
Ways to acknowledge users:
- Credit line below photos or videos
- Tagging the original creator
- Thank you post or story mention
- When reposting, clearly state the usage terms
Crediting is a requirement. It ensures fairness and avoids confusion over ownership.
5. Use Tools to Collect and Organise UGC Faster
Manual collection is manageable on a small scale, but as submissions increase, it becomes more difficult to track. This is where tools and platforms can help to centralize everything.
Tools that help:
- Social listening tools for mentions
- Submission management tools
- Use CRM or customer inbox tools to sort content
- Software that tracks campaign output
This cuts down on manual labor hours and ensures that all user generated content remains tied to actual marketing results and not just guesswork.
6. Keep Permissions Simple and Avoid Legal Confusion
Before reposting, get permission from the original creator. A single confirmation message or a brief disclosure note in the request is usually sufficient. This protects both parties and prevents problems later.
User Generated Content Examples
User generated content marketing is not restricted to just one format. Customers give feedback in a variety of ways depending on how they interact with a product, service, or experience. Some formats, such as review requests, have been established, whereas others occur naturally without the brand’s intervention. The following are examples that most businesses can implement without increasing workload or budget.
1. Reviews and Written Feedback
Written feedback is the most common type of user generated content. It helps visitors make decisions and gives them something to rely on before making a purchase. Even short, one-sentence reviews are beneficial because they address genuine concerns rather than repeating brand language.
2. Customer Photos and Real-Life Product Shots
Photos taken by actual users show how a product appears without brand lighting, filters, or promotional edits. This works when a brand prioritizes authenticity over aesthetics.
3. Quick Videos, Unboxings, and Try-Ons
Short videos of customers demonstrating how they use a product or what they received can be repurposed across multiple channels. These work because they feel genuine rather than scripted. They also provide usage instructions without watching an extensive tutorial on how to utilize the brand.
4. Experience Threads and Mini Case Examples
Some users post short summaries of their experiences on social media or community forums. These are informal but effective, especially when the product solves a problem. A brand can break these down into shorter lines for easier placement in marketing materials.
5. Q&A Responses and Informal Advice
Sometimes user generated content marketing is not a post, but rather a comment that answers another user’s question. These responses are useful because they remove doubts in a conversational rather than salesy tone. They act as peer recommendations.
6. Hashtag Campaign Entries
When users post with a campaign hashtag, it is easier to track participation and curate content. These campaigns do not always require prizes or incentives. A single repost or feature is enough to motivate many users.
7. Screenshots as Proof
A screenshot of a result, review, message, or comment is still considered user generated content. It is simple and requires little effort, which is why it works well. Screenshots are very helpful in digital offerings as well as performance results.
8. Customer Tips and User-Created Guides
Some users create short guides or tips based on their personal experiences. Brands can use these without altering the tone or structure. Guides perform best when left in the user’s language rather than rewritten to sound corporate.
Common Mistakes in User Generated Content Marketing
User generated content marketing is effective, but many brands lose momentum because they approach it with ambiguous goals or disorganized processes. Avoiding a few common mistakes can help you maintain consistency and get more out of what your customers are already sharing.

1. Wanting Polished Content Instead of Real Experiences
Many brands wait for content that looks like an advertisement. Real customers use simple formats. This should be accepted as valid content.
2. No Clear System for Permissions and Credit
Some brands repost content without verifying the usage rights. A quick permission request and a consistent credit line are sufficient to keep things clean and transparent.
3. Posting UGC Only Once and Not Repurposing It
Reusing UGC across ads, websites, emails, communities, and landing pages improves its performance. Repurposing needs planning, not production in volume.
4. Assessing Engagement Instead of Outcomes
Likes, shares, and comments do not measure impact. The emphasis should be on outcomes such as conversions, sign-ups, and assisted influence.
5. Asking for UGC Without a Clear Prompt
Users interact better when the brand directs them on what to share, where to send it, and how it will be used. A single sentence of instruction is usually sufficient.
6. Treating UGC Like an Isolated Campaign
UGC performs best when integrated into the main marketing flow. This could include collecting weekly, reviewing monthly, and distributing consistently.
Conclusion
User generated content marketing is a proven method to increase trust, reduce doubts, and drive conversions. It doesn’t require large production budgets or frequent shoots. It calls for structure, clarity, and a place for customers to share their existing experiences. The more a brand organises, repurposes, and measures user generated content, the more it contributes to growth.
Sharing, collecting, and crediting motivate customers to participate in decision-making. Reusing that voice is important, and measuring verifies that it works. When all three steps come together, UGC becomes a reliable system.
FAQs
What is UGC with an example?
User generated content refers to any content that customers create based on their interactions with a brand. It could be pictures, videos, reviews, or short posts. For example, a customer sharing a product trial video or tagging a brand in a review can be used for user generated content marketing purposes.
Is user generated content marketing expensive?
User generated content marketing is usually inexpensive because the content is created by real users rather than production teams. The cost depends on how it is collected, credited, and repurposed. Some brands invest in tools to organize submissions or track performance, but overall, UGC is less expensive than traditional content or large paid campaigns.
What is the purpose of user generated content?
The goal of User Generated Content (UGC) is to build trust, authenticity, and social proof by displaying real-world customer experiences. It helps brands to connect with audiences more organically than traditional advertisements. User generated content marketing builds credibility, influences purchasing decisions, and promotes community-driven marketing that is relatable and real.



