Understanding how users move through an e-commerce funnel makes it easier for brands to see what drives sales and where customers drop off. Instead of guessing why a product page isn’t converting or why carts are abandoned, the funnel breaks this journey into clear stages. This helps teams improve each step, whether it’s the first click, comparison stage, or checkout. Many growing brands use analytics platforms, heatmaps, or even performance marketing software to make these decisions faster and with better accuracy.
The e-commerce funnel also shows how small tweaks can increase conversions. Most businesses use this structure to acquire customers and keep them engaged long enough to complete a purchase and come back again.
What is an e-Commerce Funnel?
An e-commerce funnel explains how a shopper becomes a customer. It shows the entire journey from landing on a website to finally making a purchase. Instead of analyzing traffic and sales separately, the funnel connects the two by showing how users progress through the buying journey. This makes it easier to see which stage performs well and which one needs improvement.
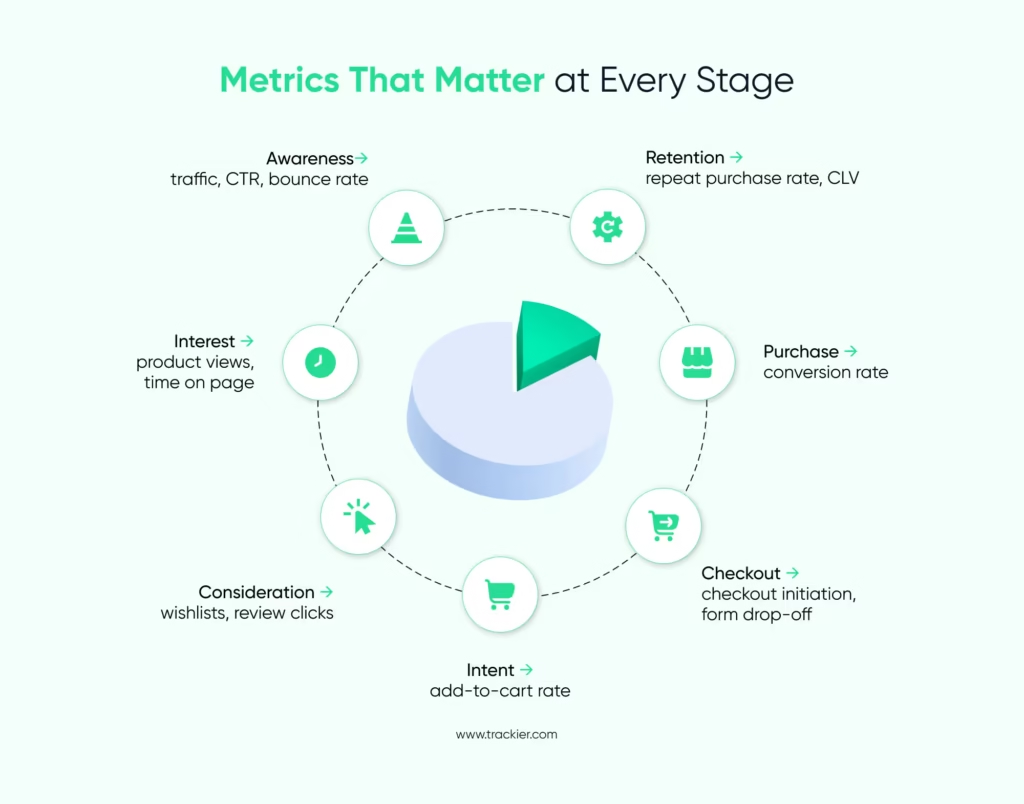
The funnel is often divided into awareness, interest, consideration, intent, purchase, retention, and advocacy. Each stage represents a user action, such as viewing a product, adding it to the cart, or checking out. When these funnel actions decrease, it indicates friction or a missing element in the user experience.
Many people confuse an e-commerce sales funnel with an e-commerce marketing funnel, but both serve different purposes. A sales funnel focuses on the steps that lead to revenue. A marketing funnel focuses on the channels and content that bring users into the journey. When both align, businesses get a better picture of what influences conversions and how visitors behave.
Most brands use funnel tracking to identify issues like low product-page engagement or high cart abandonment. With this visibility, they can adjust pages, messaging, and offers to move users smoothly to the next stage. This structure becomes even more important as customer expectations change and competition increases.
Why the e-Commerce Funnel Matters for Growth
The e-commerce funnel helps businesses understand how users behave at each stage of their buying journey. Without such a funnel, teams not only make decisions based on assumptions but also miss opportunities. A clear funnel shows where visitors lose interest, which pages cause friction, and which actions lead to revenue. This makes improvements easier and more structured.
One of the biggest advantages of using an e-commerce conversion funnel is being able to measure performance stage by stage. For example, a store might get high traffic but low add-to-cart rates. Another store may have a healthy add-to-cart rate but low checkout completion. These patterns point out what needs attention, whether it’s product information, pricing, delivery details, or checkout design.

A reliable Statista summary shows that mobile commerce drives the majority of retail website visits worldwide, which means businesses should focus on mobile-first browsing and product discovery. This supports better decisions about page layouts, load speed, and content placement across devices.
A defined e-commerce marketing funnel also improves retention. Returning customers usually convert faster and spend more, so analyzing post-purchase behavior is important. When businesses understand how to guide users from their first visit to repeat purchase, their growth becomes more predictable and sustainable.
e-Commerce Funnel Stages
The e-commerce funnel is based on the steps that customers take before and after making a purchase. Each stage shows how users interact with a store, what information they look for, and what stops them from moving forward. Teams that understand these stages can enhance the entire journey, thereby increasing conversions. Below is a breakdown of every stage and what businesses should focus on.
1. Awareness Stage
The awareness stage starts when a shopper discovers a brand for the first time. This can happen through search engines, social media, paid ads, influencers, or recommendations. Most users at this point are not ready to make a purchase and usually want basic information about the products.
Brands need to ensure they appear in relevant searches, create helpful content, and maintain active channels. A clean homepage, clear messaging, and quick-loading pages help users stay longer.
Metrics to track: Impressions, reach, click-through rate, and new website visits show how well the awareness stage is performing.
2. Interest Stage
When users get familiar with a certain brand, they begin to learn more about it. This includes browsing category pages, reading product descriptions, or checking brand reviews. At this stage, the goal is to keep users interested enough to understand what the business offers.
Product quality, images, descriptions, and FAQs affect how users perceive the store. Features like search filters, category structure, and page speed all make a lot of difference.
Metrics to track: Time on site, product views, scroll depth, and engagement with product content.
3. Consideration Stage
In the consideration stage, users start comparing products, prices, features, and alternatives. They are looking for proof that the product is worth buying. This is where social proof becomes useful. Reviews, ratings, customer photos, size guides, and comparison charts reduce confusion and build trust.
Many users also check return policies, shipping timelines, and guarantees before moving forward. These pages should be simple to navigate. Clear information helps avoid drop-offs.
Metrics to track: Return visitors, repeat product views, wishlist activity, and comparison tool usage reflect how well this stage works.
4. Intent Stage
The intent stage becomes visible when a user adds an item to their cart or takes actions that indicate buying interest. This becomes a sensitive point in the e-commerce sales funnel as users are closer to purchasing, but several factors can interrupt them.
Transparent pricing, clear shipping information, multiple payment options, and delivery timelines all help reduce the hesitation. Reminder emails, cart summaries, and low-stock alerts also help users move one step ahead.
Metrics to track: Add-to-cart rate, cart abandonment rate, and checkout initiations show whether users feel confident to proceed.
5. Purchase Stage
The purchase stage focuses on completing the transaction. Checkout should be easy, quick, and stable across all devices. Long forms, a limited number of payment methods, and unexpected costs often lead to drop-offs. According to the Baymard Institute, the most common reason for cart abandonment is extra costs like shipping and taxes.
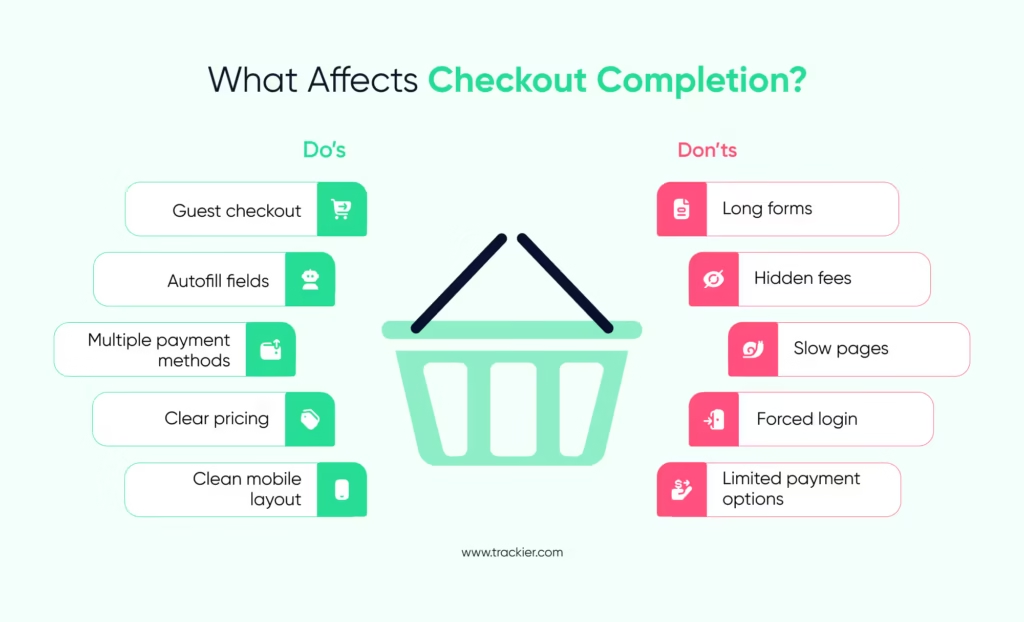
Brands should reduce friction by offering guest checkout, autofill options, trusted payment badges, and a clean layout. Upsells and cross-sells can be included here but should not distract or delay the user.
Metrics to track: Checkout completion rate, payment success rate, and revenue per visitor.
6. Retention Stage
Retention is all about keeping customers engaged after they have made a purchase. Many users buy once and never return, so post-purchase communication becomes important. Emails, loyalty programs, reorder reminders, and personalized recommendations encourage users to return.
Fast shipping, easy returns, and responsive customer support also increase retention. Brands that provide ongoing post-purchase benefits often see higher lifetime value.
Metrics to track: Repeat purchase rate, subscription sign-ups, email engagement, and customer lifetime value reflect retention strength.
7. Advocacy Stage
Advocacy happens when satisfied customers share their experience with others. This can include reviews, ratings, user-generated content, social media posts, or referrals. Advocacy builds trust because people base their purchasing decisions on real experiences.
Referral rewards, encouraging reviews, and highlighting customer stories help grow this stage. Advocacy also supports the awareness stage, bringing in more users organically.
Metrics to track: Referral traffic, review volume, ratings, and social mentions.
E-Commerce Funnel Metrics You Must Track
Tracking the right e-commerce funnel metrics shows how well each stage performs and which improvements have the highest impact on revenue. Here are the key metrics that every business should track.
1. Traffic Quality
Traffic quality shows whether the right users are visiting your site. High traffic does not always mean high sales. If visitors do not match your target audience, engagement and conversions will be very low.
Key metrics: new users, returning users, source-based sessions, bounce rate, and device split.
2. Product Page Engagement
Product pages influence customer interest and intent. Poor engagement means weak descriptions, slow loading, or unclear information.
Key metrics: product views, scroll depth, image clicks, time on product pages, and exit rate.
3. Add-to-Cart Rate
This metric reveals how many users are confident enough to move from browsing to intent. A low add-to-cart rate usually indicates problems with pricing, product clarity, or trust signals.
Formula: Add-to-cart actions / Total product page sessions x 100.
4. Cart Abandonment Rate
A key metric in any e-commerce conversion funnel. A high abandonment rate shows friction in pricing, checkout design, or delivery details.
Formula: (Carts created – Purchases completed) / Carts created x 100.
5. Checkout Completion Rate
This indicates the number of users who start checkout actually finish it. Even small delays or lengthy forms can reduce completion. Multiple payment options, guest checkout, and a simple layout will help.
Formula: Completed checkouts / Checkout initiations x 100.
6. Purchase Rate
Purchase rate shows how many users turn into customers. It reflects the overall strength of your e-commerce sales funnel, because it combines product, pricing, and experience.
Formula: Purchases / Total sessions x 100.
7. Average Order Value (AOV)
AOV measures the average amount spent per transaction. It helps businesses understand buying patterns and identify opportunities for bundles or add-ons.
Formula: Total revenue / The number of orders.
8. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
CLV shows how much a customer is likely to spend during a lifetime with the brand. Higher CLV usually means strong retention and a positive buying experience.
Formula: (Average order value x Purchase frequency) x Average customer lifespan.
9. Repeat Purchase Rate
This metric shows how many of your customers are returning for repeat buys. A high repeat purchase rate means your retention stage is strong.
Formula: Returning customers / Total customers x 100.
10. Refund and Return Rate
This tells you how often users return products. A high return rate usually indicates unclear descriptions, sizing issues, or quality concerns.
Formula: Returned orders / Total orders x 100.
How to Build a High-Converting E-Commerce Conversion Funnel
A strong e-commerce funnel is built by improving every stage of the buying process. Users should be able to discover the brand, explore products, make decisions, and complete their purchase with each. The following are practical steps that can increase conversions and create a smooth buying experience.
1. Strengthen Top-of-Funnel Visibility
At the awareness stage, users need clear paths to find your store. This includes appearing in search results, social feeds, and relevant communities.
What to focus on:
- SEO-friendly product pages
- Active social content
- Paid ads targeting high-intent audiences
- Fast-loading mobile pages
These steps help bring better users into your e-commerce marketing funnel.
2. Improve Product Discovery
Once users land on the site, they should be able to view products easily. Clean navigation, well-organized categories, and strong filters help visitors explore without confusion.
What to focus on:
- Clearly grouped product
- Relevant search filters
- On-site search bar
- High-quality images and uniform layouts
Simple structures reduce drop-offs and encourage product exploration.
3. Optimize Product Pages
Product pages have a significant impact on buying decisions. Incomplete or unclear information leads to hesitation.
What to focus on:
- Descriptive details
- Diverse photos and videos.
- Size charts
- Reviews and ratings
- Shipping and return information
- Price transparency
These improvements push users from interest to consideration.
4. Create Strong Trust Signals
Trust has an impact on conversions across all funnel stages. Even if traffic is high, users will not add items to their cart unless they believe in the brand.
What to focus on:
- Secure payment badges
- Customer reviews
- Brand guarantees
- Clear policies
- Real customer photos
Trust signals encourage more people to add items to their carts and start checking out.
5. Reduce Friction in the Cart Stage
The cart stage shows intent. Any friction here increases abandonment.
What to focus on:
- Pre-calculated shipping costs
- Easy cart editing
- Saved cart options
- Reminder emails
- Stock and offer reminders
- Clean UI on mobile and desktop
This helps users continue toward checkout.
6. Simplify the Checkout Flow
The checkout process should be quick and distraction-free. This is one of the most sensitive stages in the e-commerce conversion funnel.
What to focus on:
- Guest checkout
- Autofill fields
- Multiple payment methods
- Fewer form fields
- Clear error messages
- Transparent final pricing
These steps help improve checkout completion rate and reduce page exits.
7. Improve Post-Purchase Experience
Retention supports long-term growth. A user who returns to buy again increases customer lifetime value and stabilizes revenue.
What to focus on:
- Order tracking updates
- Fast delivery
- Easy returns
- Personalised recommendations
- Loyalty programs
- Responsive customer support
A strong post-purchase stage improves repeat purchase rate and brand trust.
8. Encourage Advocacy
Happy customers are more likely to share their experience, which supports top-of-funnel growth.
What to focus on:
- Review requests
- Referral programs
- User-generated content
- Reward points
- Social sharing options
Advocacy strengthens the funnel and reduces acquisition costs.
E-Commerce Funnel Optimization Strategies
Improving an e-commerce funnel is about reducing friction at every stage and helping users move through the buying journey with ease. The goal is to make product discovery easier, build trust early, and create a smooth checkout experience. These strategies help you improve conversions across the entire funnel.
1. Strengthen Your Homepage and Navigation
Your homepage and top navigation help users to the right products. Add clear categories, search filters, and visible CTAs. Make sure users can get to the product pages within two to three clicks. A simple and predictable structure reduces early drop-offs.
2. Improve Product Discovery
Users should find relevant items quickly. Add filters, sorting options, “related products,” and personalised recommendations. A strong search bar with auto-suggestions also improves product discovery, especially for stores with large catalogues.
3. Optimise Product Pages
Product pages influence most buying decisions.
Improve the following elements:
- High-quality photos and videos
- Clear pricing
- Sizing guides and specifications
- Bullet-point descriptions
- Reviews and ratings
- Estimated delivery dates
These details help users evaluate products faster and reduce hesitation.
4. Encourage Add-to-Cart Actions
Make your “Add to Cart” button visible, bold, and easy to spot. Use clear CTAs, offer limited-time discounts, and highlight bestsellers. Provide transparent pricing to avoid negative surprises later.
5. Reduce Cart Abandonment
Cart abandonment happens when users face hidden costs, slow loading pages, or confusing checkout steps. Display upfront shipping fees, estimated delivery time, and return policies. Offer guest checkout and multiple payment options.
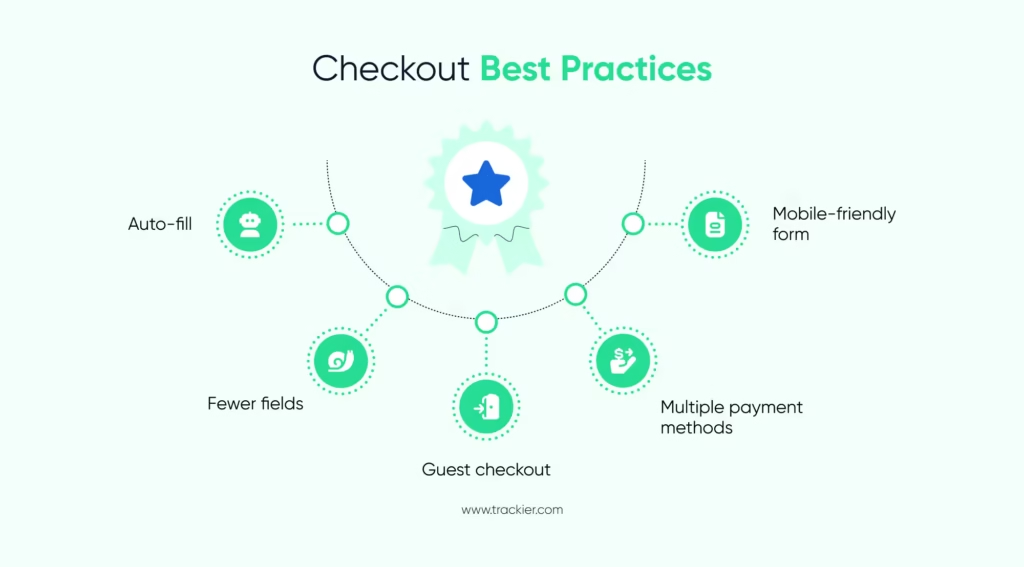
6. Improve Checkout Flow
A simple checkout improves conversion rates. Reduce form fields, allow auto-fill, and keep the process on one page if possible. Provide popular payment methods, including digital wallets and UPI. Ensure that the mobile checkout experience is as smooth as the desktop.
7. Use Email and SMS Automation
Automate abandoned cart reminders, price drop, and back-in-stock notifications. Users often return when reminded at the right time. Keep messages short and include a direct link to the cart or product page.
8. Add Trust-Building Elements
Trust is essential for guiding users through the funnel.
Include:
- Secure payment badges
- Return policy highlights
- Warranty information
- Social proof and real photos
- Transparent shipping details
Clear trust signals help users feel confident while completing a purchase.
9. Improve Page Speed
A slow page delays every stage of your funnel. Compress images, remove unnecessary scripts, and optimise mobile layout. Even small speed improvements reduce bounce rates and increase conversions.
10. Personalise the User Journey
Personalised recommendations, dynamic product lists, and targeted offers help users find relevant items faster. Personalisation also increases AOV and repeat purchases.
E-Commerce Funnel vs Traditional Sales Funnel
E-commerce funnels and traditional sales funnels follow a similar structure, but the customer journey and conversion triggers differ. The e-commerce path is faster, more self-directed, and depends heavily on on-site experience and performance. Traditional funnels usually involve longer decision cycles, multiple touchpoints, and direct communication between the buyer and the seller.
1. Speed of Decision-Making
E-commerce decisions often happen within minutes. Customers browse, compare, add to cart, and pay without speaking to anyone. Traditional sales usually involve calls, demos, or meetings.
2. Level of Buyer Interaction
E-commerce funnels rely on product pages, reviews, checkout flow, and digital triggers. Traditional funnels depend heavily on relationship-building and sales representatives.
3. Number of Users
E-commerce funnels handle higher traffic volumes and shorter interactions. Traditional funnels focus on fewer leads with greater engagement.
4. Data Availability
E-commerce funnels provide real-time behavioural data such as clicks, scrolls, exit points, and drop-offs. Traditional funnels track data manually or through CRM inputs.
5. Purchase Process
E-commerce conversions happen through automated online checkout. Traditional funnels often require approvals, contracts, and longer nurturing cycles.
Understanding these differences helps you create the right e-commerce conversion funnel and avoid applying outdated sales funnel methods to online-first users.
Tools to Track and Optimize Your E-Commerce Funnel
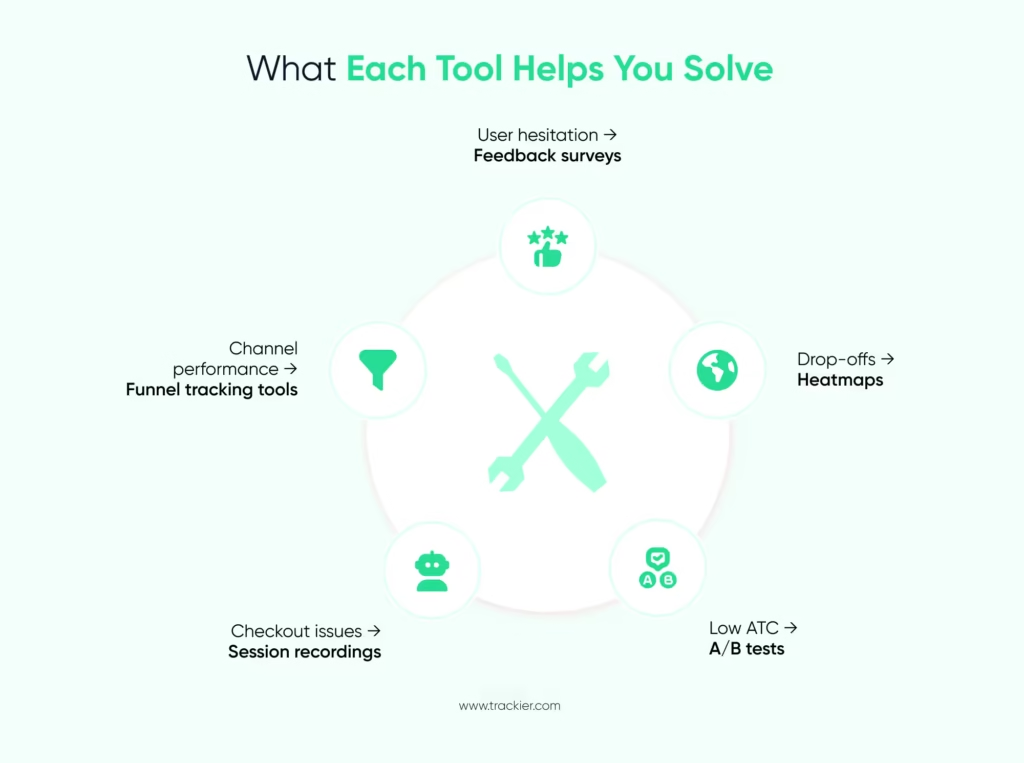
Tracking an e-commerce funnel requires a combination of analytics, behavioural tools, integrations, and performance tracking solutions. These help you understand user intent, identify friction, and increase conversion rates. Many brands also use tools similar to performance marketing software to track channel efficiency and optimise campaign spending.
1. Google Analytics & GA4
Useful for tracking traffic sources, session paths, funnel stages, drop-offs, and conversions. GA4 also supports event-based tracking, which is necessary for understanding e-commerce funnel metrics accurately.
2. Heatmap and Behaviour Analytics Tools
Tools like Microsoft Clarity show scroll patterns, clicks, hesitation points, and sections that users skip. They highlight UX issues that standard analytics cannot reveal.
3. A/B Testing Tools
Platforms like VWO or Optimizely help test product page layouts, CTA positions, images, and checkout flow variations to see what improves conversions.
4. Session Recording Tools
These tools show real user sessions so you can identify where customers drop off. Useful for spotting broken elements, slow-loading sections, or confusing steps.
5. Customer Feedback Tools
Surveys and review widgets help you understand why users hesitate or abandon purchases. Even quick pop-ups asking, “What stopped you from checking out?” can reveal information you can work on.
6. Marketing Automation Tools
Helps you send personalised emails, abandoned cart reminders, upsell campaigns, and post-purchase follow-ups.
7. Funnel Tracking Tools
Platforms designed for affiliate tracking or performance marketing also help brands understand which channels attract qualified buyers, which campaigns leak revenue, and where to optimise spending.
Common E-Commerce Funnel Mistakes to Avoid
Many funnel issues come from small gaps in UX, messaging, or tracking. Fixing these mistakes can quickly improve conversions without major redesigns or budget increases.
1. Too Many Steps in the Checkout Flow
Long forms and multiple screens increase drop-offs. Keep checkout short, mobile-friendly, and only ask for necessary information.
2. Unclear Pricing or Hidden Charges
Unexpected fees are one of the biggest reasons for cart abandonment. A Baymard Institute study shows that 39% of users abandon carts due to high extra costs.
3. Slow Page Load Time
Even a one-second delay can result in fewer conversions. Slow pages disrupt user flow and create friction at every stage.
4. Weak Product Descriptions
Users are confused by product information that is either too short or too unclear. Strong copy reduces hesitation and improves the add-to-cart rate.
5. Poor Mobile Experience
If the site is difficult to scroll, navigate, or check out on mobile devices, users will drop off quickly.
6. No Clear CTAs
CTAs help users move through your e-commerce funnel. Weak or hidden CTAs leave users unsure about the next step.
7. Not Tracking the Full Funnel
Some brands only track final purchases. Without tracking discovery, product views, add-to-cart rates, and checkout starts, you miss the real reasons behind low conversions.
8. Ignoring Returning Customers
Focusing only on new customers increases CAC. Repeat buyers often convert faster and spend more.
Conclusion
A strong e-commerce funnel takes users from discovery to checkout with minimal friction. Each stage influences how customers move forward, and improving just one step can noticeably increase conversions.
Focus on clear navigation, high-quality product pages, smooth checkout process, and consistent tracking. Combine analytics with real user feedback to understand where buyers hesitate and how you can improve their journey.
With regular optimisation, your e-commerce sales funnel becomes a predictable, adaptable system for driving revenue.
FAQs
1. What is an e-commerce funnel?
An e-commerce funnel is the path that a shopper takes from discovering your store to making a purchase. It breaks the journey into several stages like awareness, consideration, product evaluation, add-to-cart, checkout, and conversion. Tracking each stage helps identify where users drop off and what needs to be improved. A well-optimised e-commerce funnel increases conversions, reduces friction, and improves the customer experience.
2. What are the 4 marketing funnels?
The four core marketing funnel stages are awareness, interest, desire, and action, also known as AIDA. These stages help brands understand how customers progress from first learning about a business to making a purchase. In e-commerce, these stages translate into discovering the store, exploring products, showing buying intent, and completing the checkout. Tracking each step ensures smoother progression and higher conversions.
3. What are the 5 stages of a sales funnel?
The five stages of a sales funnel are awareness, consideration, conversion, loyalty, and advocacy. These stages explain how a customer moves from learning about a product to becoming a repeat buyer who recommends the brand to others. For e-commerce, this includes discovering the store, evaluating products, purchasing, returning for future orders, and sharing positive experiences. It helps businesses plan long-term growth and retention strategies.



